Main Objectives
The main objectives of DECOVALEX THMC were the study of THMC processes important for PA and SA and the investigation of EDZ. This phase consisted of four BMT"e;s and 1 TC"e;s. A BMT is a Benchmark Test in which the output of different computer codes are compared for a particular problem. A TC is a Test Case in which the output of one or more computer programs are compared against reality.
BMT1: influence of near-field THM couplings on PA (Task A)
- model calibration of rock damage and bentonite models on lab tests and in-situ experiments
- THM analysis of a near field hypothetical repository
- calculation of PA indicators
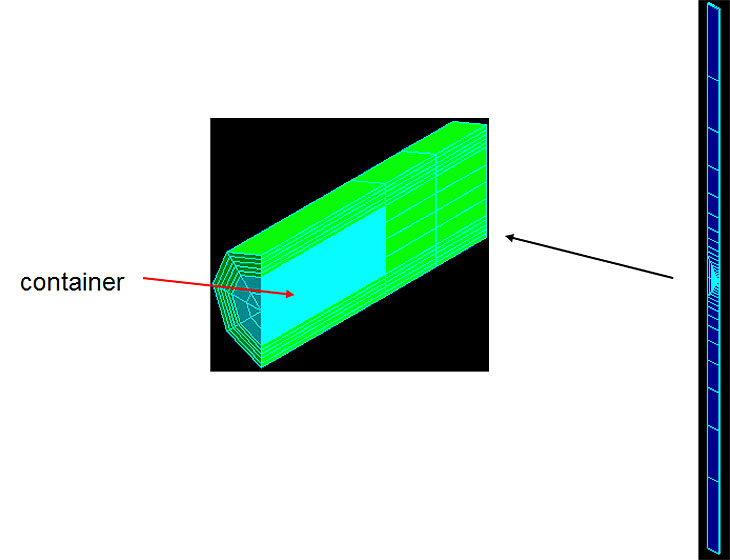
Discussion:
- overall consistent results between teams
- Possible improvement : extent and properties of EDZ
BMT2: Evolution of the EDZ in crystalline rocks (Task B)
- lab testing and modeling of mechanical strength of granite
- THMC analysis of an emplacement drift in a hypothetical repository
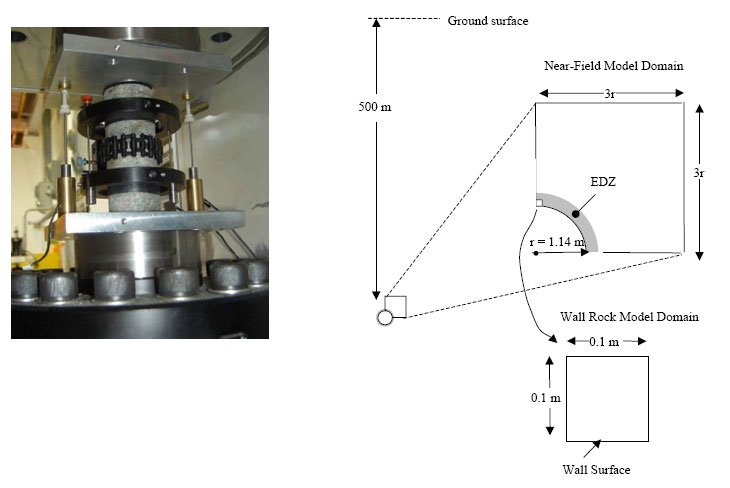
Discussion:
- variety of models used for EDZ simulation
- Possible improvement: scale and time dependant strength properties – use of micromechanics
BMT3: Long term changes in EDZ due to THM and THC processes (Task D)
- THM simulations of a Febex type ( saturated granite with buffer) and of a YM type (unsaturated tuff without buffer) repositories
- THC simulations of a Febex type and of a YM type repositories
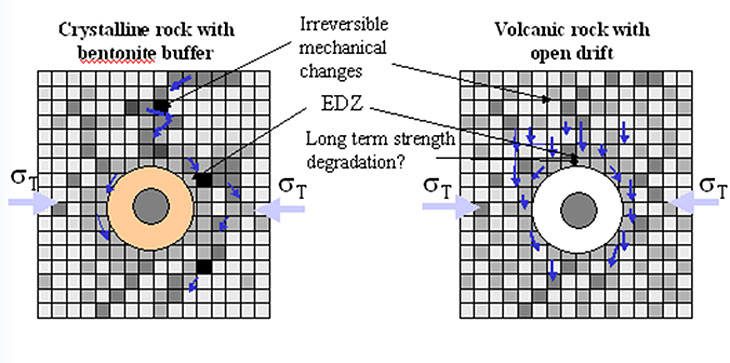
Discussion:
- overall good agreement between predictions
- Possible improvements:
- shear induced permeability changes
- accounting for reaction kinectics
- long term MC couplings
BMT4: THMC simulation of the effects of a glaciation (Task E)
- infiltration of glacial meltwaters to the subsurface
- anomalous hydraulic head
- groundwater flow under permafrost conditions
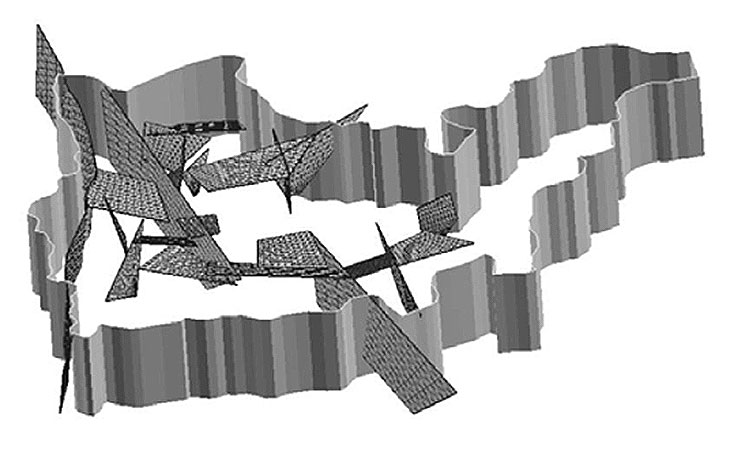
Discussion:
- shortcomings due to 2D analysis compared to 3D
- Possible improvements:
- fracture reactivation mechanisms
- coupling with reactive transport model
TC1: Evolution of the EDZ in Tournemire argillite (France)
- modelling the extent of EDZ around a 100 years old tunnel
- modelling the evolutions of EDZ around 3 openings of different ages
- modelling a mine-by-test around a 2003 gallery
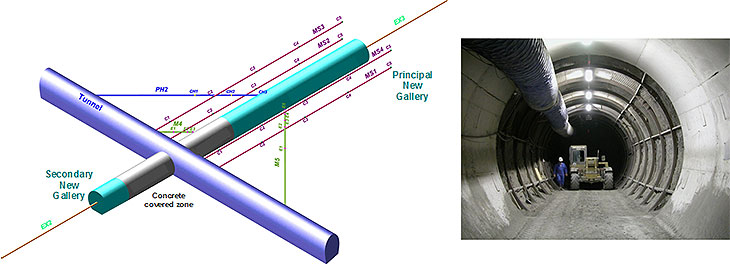
Discussion:
- instantaneous failure mechanisms well understood
- Possible improvement: modelling delayed failure mechanims
